Unlocking Raw Transactions: Understanding Ethereum’s Blockchain Architecture
When it comes to digital currencies like Ethereum, the concept of a blockchain may seem mysterious, but its underlying architecture is rooted in cryptography and secure storage. In this article, we’ll delve into how unsaved transactions are stored on the Ethereum blockchain and explore the implications of accessing these raw transactions.
What is a transaction?
In any cryptocurrency network, including Ethereum, a transaction refers to a single unit of exchange between two parties. It’s typically represented as an input and output pair, where a sender provides something (or sends something) in exchange for something else.
Blockchain Storage: A Quick Basic
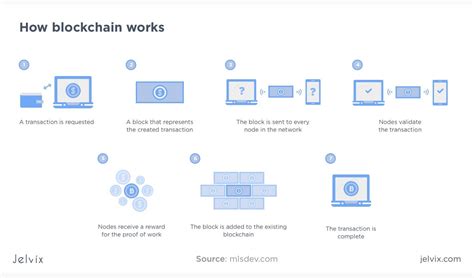
A blockchain is a decentralized, distributed ledger that records all transactions on the network. To store a transaction on the Ethereum blockchain, it must first be transformed into a hash-based format called a “block.” A block contains multiple transactions, which are then combined into a single “transaction batch.”
Raw Transactions: Double Hashing for Security
Ethereum’s primary storage mechanism is the
Ethash algorithm, also known as EthGas (Eth Gas). This hash function generates a unique digital fingerprint of the raw transaction, which is then re-hashed using SHA256 to create a
double hash.
The double-hashing format is designed to protect transactions from being modified or altered in transit. By storing the transaction hash twice, Ethereum ensures that any attempt to tamper with it would require both hashes to be identical—making it virtually impossible to tamper with the data without the network detecting it.
Here’s how it works:
- When a new transaction is created and sent to the Ethereum network.
- The transaction passes through Ethereum validator nodes (also called “miners”), who verify its validity and ensure that it complies with the blockchain’s rules.
- Once validated, the transaction is merged into a block along with other transactions.
- The block is then hashed using Ethash, creating a unique hash value for each block.
- To store the raw transaction, we need to go through the hashing process again.
Accessing Raw Transactions: A Double-Edged Sword
Now that we understand how raw transactions are stored on the Ethereum blockchain, let’s consider the implications of accessing these transactions. In theory, it would be possible to gain access to raw transactions if the double-hashed format were tampered with or if unauthorized access to the network were gained.
However, there are several reasons why this is not possible:
- Double Hashing: These two hash values are designed to be mutually exclusive, making it extremely difficult for an attacker to tamper with a transaction without being detected.
- Network Security
: The Ethereum network’s security measures, including encryption and secure communication channels (e.g. HTTPS), ensure that any attempts to access or tamper with transactions will be detected and penalized.
- Ethereum’s Gas System: The gas system allows the network to verify the integrity of each block by requiring miners to stake a certain amount of Ethereum (ETH) in exchange for verifying the transaction batch.
In conclusion, raw transactions on the Ethereum blockchain are stored using a double-hashing format, which provides robust security and prevents forgery. While it is theoretically possible to access these transactions if you had access to the network or tampered with the hashing process, this is unlikely due to the sheer complexity of the Ethereum network and its built-in security measures.
As the use of cryptocurrencies continues to grow, understanding the complexities of blockchain architecture is more important than ever.
